
Surgery may be the only treatment for a primary spinal tumor that is non-cancerous. 2 levels of hot compress, intelligent temperature control technology, continuous 42 constant temperature, deep. This type of shunt is used to treat syringomyelia. Packing list: USB charging cable, a pair of external patch, meridian line, manual, intelligent cervical massage instrumentFeatures:1.TENS low frequency pulse technology, EMS technology, deep muscle training, double pulse massage2. Syrinx to Subarachnoid ShuntĪ syrinx to subarachnoid shunt is used to restore the natural flow of cerebrospinal fluid. While fusing two vertebrae together may limit bending and twisting of the trunk, many patients feel an improvement in range of motion because their pain has been reduced. To do so, your surgeon will remove the spinal discs between. The operation enlarges this space, called the foramen. Cervical spinal fusion: This surgery may result in some lost flexibility, but it will limit painful symptoms and stabilize the spine. The guide, developed on behalf of the Australian Physiotherapy.
#Cervical spine manual
This minimally invasive surgery is used to relieve pressure on or pinching of a nerve root as it exits the spinal canal through the space between two vertebrae. Clinical guide to safe manual therapy practice in the cervical spine. A cervical laminectomy can be performed to relieve the symptoms of spinal stenosis, the narrowing of the spinal canal. Cervical LaminectomyĪ cervical laminectomy is a spine surgery that involves removing some posterior bone to relieve excess pressure on the nerves in the cervical spine, or neck. Cervical spine ligaments The cervical spine ligaments are a combination of ligaments that continue from lower regions of the vertebral column (that change names as they reach C2) and ligaments that are unique to the cervical spine. Arthroplasty (Artificial Disc)Īrthroplasty, or cervical artificial disc surgery, is a type of joint replacement procedure which involves inserting a cervical artificial disc into the intervertebral space after a cervical disc has been removed. Assessment requires a systematic approach.Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion is an operation that involves relieving the pressure placed on nerve roots, the spinal cord or both by a herniated disc or bone spurs. The lateral view is often the most informative image.
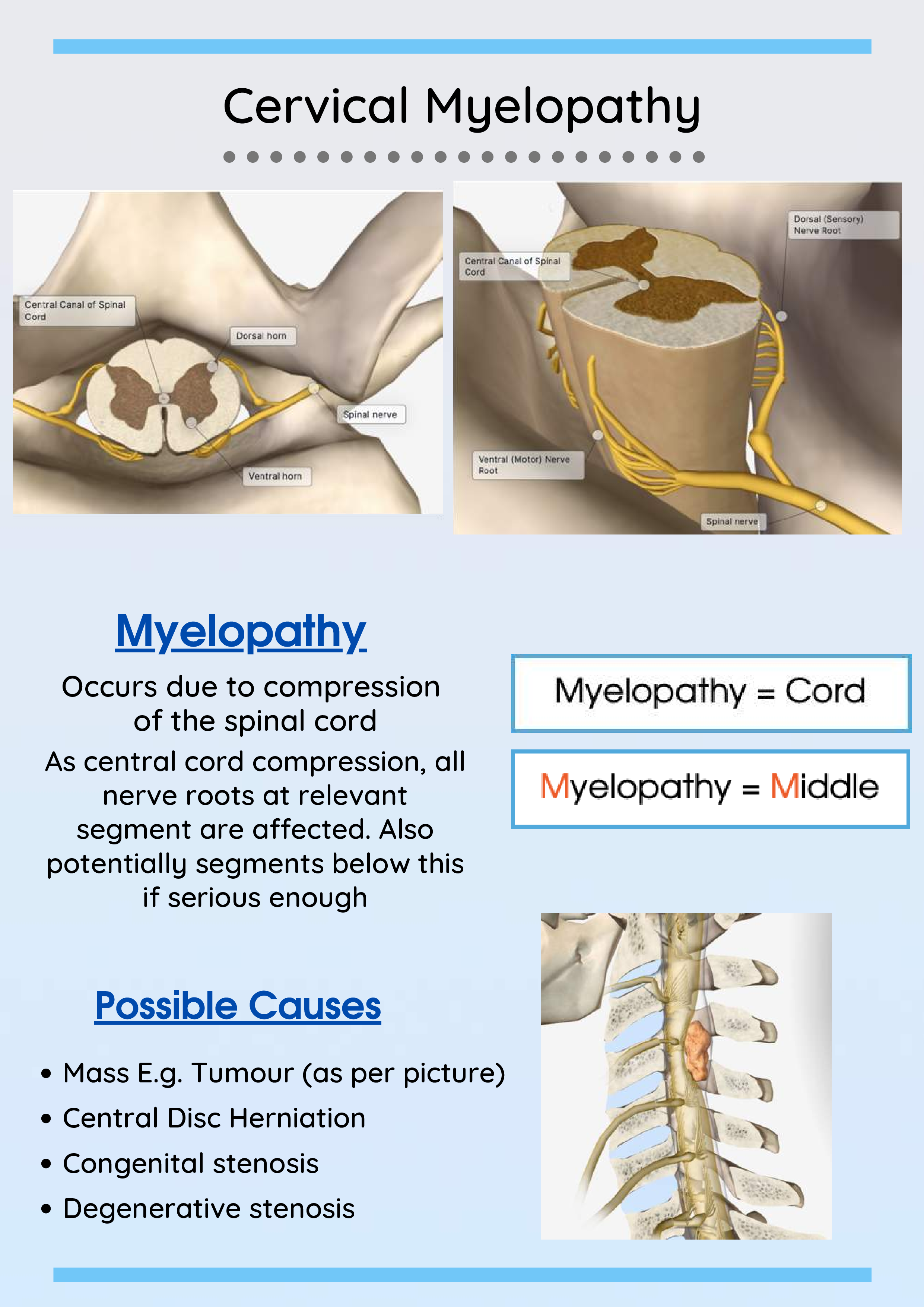
If the lateral view does not show the vertebrae down to T1 then a repeat view with the arms lowered or a ' Swimmer's view' may be required. Cervical myelopathy and/or radiculopathy are conditions caused by compression of the spinal cord (myelopathy) and/or nerve roots (radiculopathy) as they pass. In the context of trauma these images are all difficult to acquire because the patient may be in pain, confused, unconscious, or unable to cooperate due to the immobilisation devices.
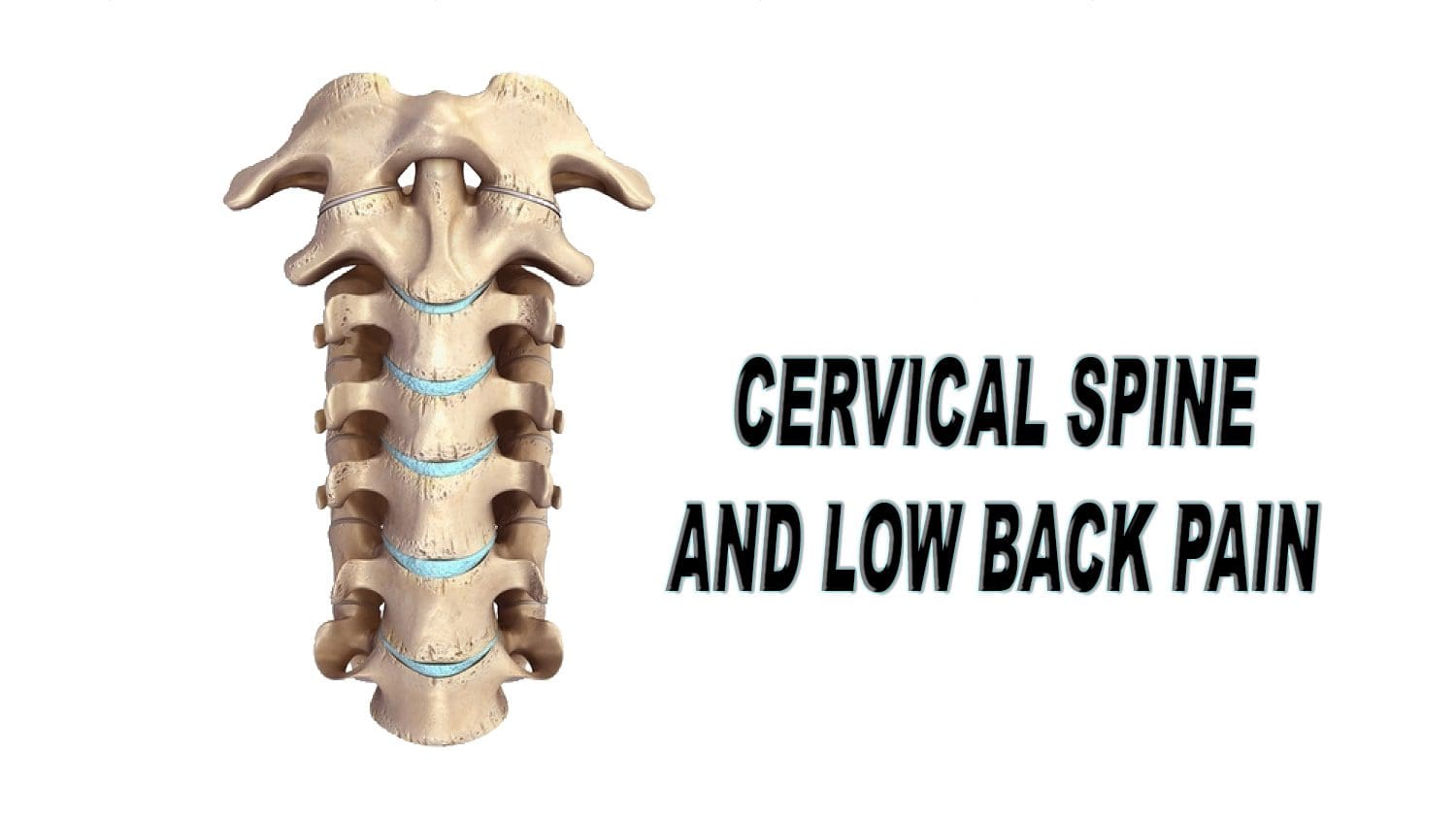
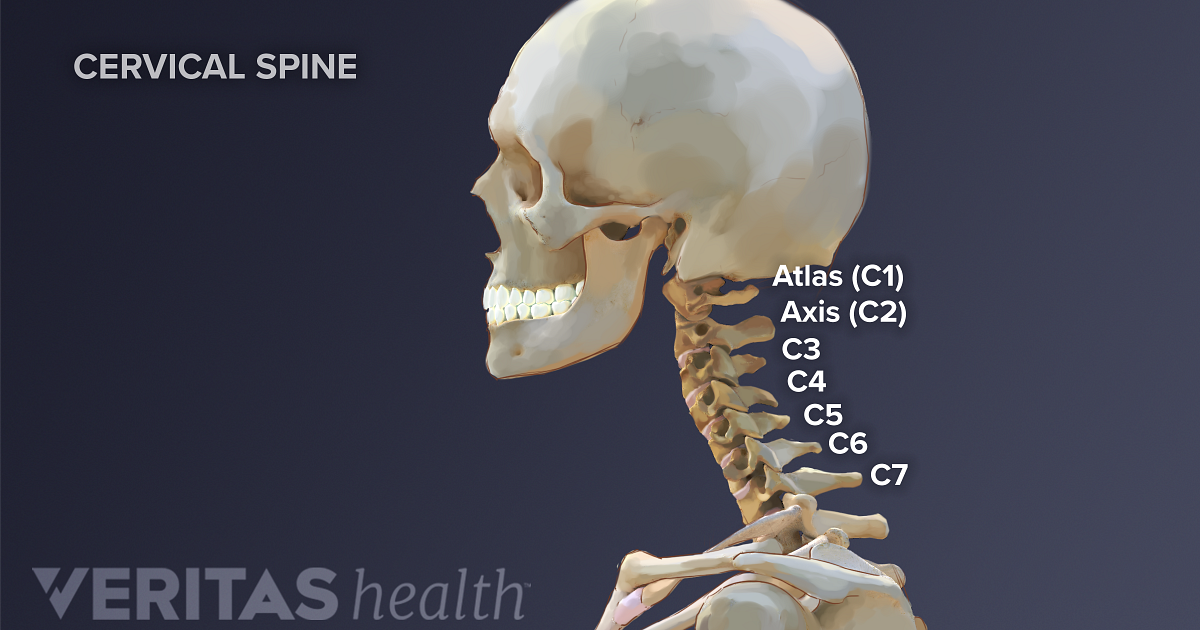
The 3 standard views are - Lateral view - Anterior-Posterior (AP) view - and the Odontoid Peg view (or Open Mouth view). Imaging should not delay resuscitation.įurther imaging with CT or MRI (not discussed) is often appropriate in the context of a high risk injury, neurological deficit, limited clinical examination, or where there are unclear X-ray findings. The cervical spine has seven stacked bones called vertebrae, labeled C1 through C7. This is because normal C-spine X-rays cannot exclude significant injury, and because a missed C-spine fracture can lead to death, or life long neurological deficit.Ĭlinico-radiological assessment of spinal injuries should be managed by experienced clinicians in accordance with local and national clinical guidelines. Bones - Cortical outline/Vertebral body heightĬlinical considerations are particularly important in the context of Cervical spine (C-spine) injury.Alignment - Anterior/Posterior/Spinolaminar.The vertebra and discs form the spinal column from. Look at all views available in a systematic manner It is made up of bony segments called vertebra with fibrous tissue called intervertebral discs between them.It is extremely important to understand the key role that the stability and. Clinical considerations are of particular importance when assessing appearances of C-spine X-rays Upper cervical spinal cord (and its connections to the trigeminal nerve) Brainstem.Normal C-spine X-rays do not exclude significant injury The C-spine consists of seven vertebrae (C1C7) and supports the weight of the head (approximately 14 pounds).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
